Properties of Boolean functions/hard/binary
| Studies of Boolean functions |
| Properties of Boolean functions | |
|---|---|
| hard | soft |
| binary | |
| integer | integer |
| permutation | permutation |
Hard properties can be assigned to a BF, without referencing its arity.
Binary properties have the values true or false, so they partition all BF into a subset and the rest.
linear
Linear Boolean functions are Walsh functions and their complements.
seal
See Seal (discrete mathematics). Seal block is a broader property.
dense
no gaps before or between the atoms, i.e. valency = adicity (often called nondegenerate)
strong
BF is strong, iff strength = adicity, so its family has the biggest possible size 2adicity.
balanced
same number of true and false places, i.e. weight = 0.5
BF that are not balanced are light or heavy, i.e. their weight is below or above 0.5.
openness
| family | clan | |
|---|---|---|
| closed | unopen | |
| unclosed | ajar | |
| open |
- BF is closed, iff complement is in same family, otherwise unclosed. Self-complementary families are closed.
- BF is unopen, iff complement is in same clan, otherwise open. Self-complementary clans are unopen.
- BF is ajar, iff complement is in same clan, but not in same family
monotonic
no true place under false place (when places are arranged in a Hasse diagram) (counted by Dedekind numbers)
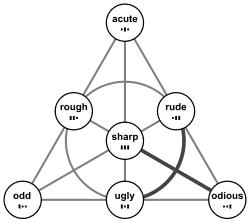
related to parity
| even evil (0) | even odious (2) |
| odd evil (1) | odd odious (3) |
- parity: BF is odd/even iff first place in truth table is true/false. Same as parity of the Zhegalkin index.
- depravity: BF is odious/evil iff last place in truth table is true/false. Same as parity of the binary weight of the Zhegalkin index.
- BF is ugly, iff parity and depravity are different (i.e. iff the quadrant is 1 or 2).
- quadrant = parity + 2 · depravity
| images for arity 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| odd | odious | ugly | quadrants | ||
| truth tables |
.svg.png) 1 1000 0000 |
.svg.png) 128 0000 0001 |
.svg.png) 129 1000 0001 |
 |
 |
| Zhegalkin indices |
.svg.png) 255 1111 1111 |
.svg.png) 254 0111 1111 |
.svg.png) | ||
- gender: BF is male/female, iff its root is sharp/blunt. See Gender of Boolean functions.
honesty
BF is honest/dishonest, iff the XOR of all members of its family is the tautology/contradiction. (Most BF are honest.)